Slide 15 of 26
Notes:
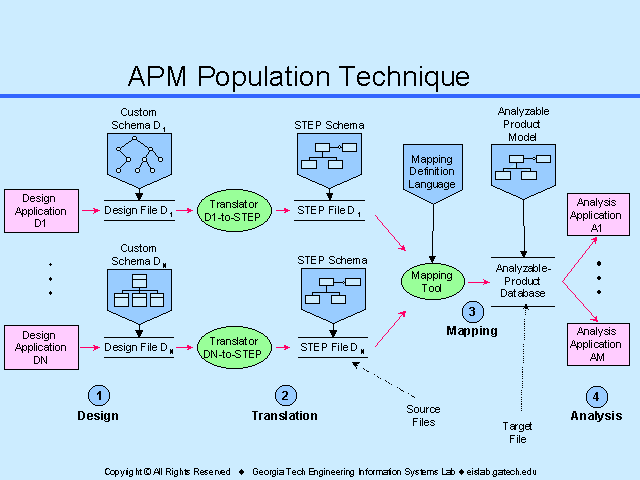
- This slide is a diagram of the APM population technique.
- This is a general version of what we have already seen for TIGER.
- The purpose of this technique is to populate the APM with design data spanning several design sources, in order to support the information requirements of the analysis modules downstream.
- The technique consists of four steps:
- 1. Design: design applications (D1 to DN) generate data about various aspects of the product and store it in files with custom data structures and formats (shown in the figure as Design Files D1 to DN, conforming to Custom Schemas D1 to DN).
- 2. Translation: each custom design file is translated into a neutral format (STEP, shown as STEP Files D1 to DN).
- 3. Mapping: data spanning different STEP files is integrated into a single repository (the Analyzable Product Database, or APD, which conforms to the APM).
- 4. Analysis: finally, analysis applications (A1 to AM) retrieve the data they need from the APD.